
User's Manual
 |
|
| Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor User's Manual |
|
18. Rabbit Instructions
Summary
All bugs related to instructions have been fixed in revisions A-C of the Rabbit 2000 chip. See Appendix B for more information.
Detailed information on instructions in provided in this chapter.
"Load Immediate Data" on page 178
Spreadsheet Conventions
"8-bit Indexed Load and Store" on page 178
"16-bit Indexed Loads and Stores" on page 178
"16-bit Load and Store 20-bit Address" on page 179
"Register to Register Moves" on page 179
"Exchange Instructions" on page 180
"Stack Manipulation Instructions" on page 180
"16-bit Arithmetic and Logical Ops" on page 180
"8-bit Arithmetic and Logical Ops" on page 181
"8-bit Bit Set, Reset and Test" on page 182
"8-bit Increment and Decrement" on page 182
"8-bit Fast A register Operations" on page 183
"8-bit Shifts and Rotates" on page 183
"Instruction Prefixes" on page 184
"Block Move Instructions" on page 184
"Control Instructions - Jumps and Calls" on page 185
"Miscellaneous Instructions" on page 185
"Privileged Instructions" on page 186
"Instructions in Alphabetical Order With Binary Encoding" on page 189
ALTD ("A" Column) Symbol Key Flag Description ALTD selects alternate flags
ALTD selects alternate flags and register
ALTD selects alternate register
ALTD operation is a special case
IOI and IOE ("I" Column) Symbol Key Flag Description IOI and IOE affect source and destination
IOI and IOE affect destination
IOI and IOE affect source
Flag Register Key S Z L/V 1 C Description Sign flag affected
Sign flag not affected
Zero flag affected
Zero flag not affected
LV flag contains logical check result
LV flag contains arithmetic overflow result
LV flag is cleared
LV flag is affected
Carry flag is affected
Carry flag is not affected
Carry flag is cleared
Carry flag is set
1 The L/V (logical/overflow) flag serves a dual purpose--L/V is set to 1 for logical operations if any of the four most significant bits of the result are 1, and L/V is reset to 0 if all four of the most significant bits of the result are 0.
Symbols
Rabbit Z180 Meaning Bit select:
000 = bit 0, 001 = bit 1,
010 = bit 2, 011 = bit 3,
100 = bit 4, 101 = bit 5,
110 = bit 6, 111 = bit 7
Condition code select:
00 = NZ, 01 = Z,
10 = NC, 11 = C
7-bit (signed) displacement. Expressed in two's complement.
Word register select destination: 00 = BC, 01 = DE, 10 = HL, 11 = SP
Word register select alternate: 00 = BC', 01 = DE', 10 = HL'
8-bit (signed) displacement added to PC.
Condition code select:
000 = NZ (non zero), 001 = Z (zero),
010 = NC (non carry), 011 = C (carry),
100 = LZ1 (logical zero), 101 = LO2 (logical one),
110 = P (sign plus), 111 = M (sign minus)
MSB of a 16-bit constant.
16-bit constant.
8-bit constant or LSB of a 16-bit constant.
Byte register select:
000 = B, 001 = C,
010 = D, 011 = E,
100 = H, 101 = L,
111 = A
Word register select (source): 00 = BC, 01 = DE, 10 = HL, 11 = SP
Restart address select:
010 = 0x0020, 011 = 0x0030,
100 = 0x0040, 101 = 0x0050,
111 = 0x0070
Word register select: 00 = BC, 01 = DE, 10 = IX, 11 = SP
Word register select: 00 = BC, 01 = DE, 10 = IY, 11 = SP
Word register select: 00 = BC, 01 = DE, 10 = HL, 11 = AF
1 Logical zero if all four of the most significant bits of the result are 0.
2 Logical one if any of the four most significant bits of the result are 1.
18.1 Load Immediate Data
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
LD IX,mn 8 - - - - IX = mn
LD IY,mn 8 - - - - IY = mn
LD dd,mn 6 r - - - - dd = mn
LD r,n 4 r - - - - r = n18.2 Load & Store to Immediate Address
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
LD (mn),A 10 d - - - - (mn) = A
LD A,(mn) 9 r s - - - - A = (mn)
LD (mn),HL 13 d - - - - (mn) = L; (mn+1) = H
LD (mn),IX 15 d - - - - (mn) = IXL; (mn+1) = IXH
LD (mn),IY 15 d - - - - (mn) = IYL; (mn+1) = IYH
LD (mn),ss 15 d - - - - (mn) = ssl; (mn+1) = ssh
LD HL,(mn) 11 r s - - - - L = (mn); H = (mn+1)
LD IX,(mn) 13 s - - - - IXL = (mn); IXH = (mn+1)
LD IY,(mn) 13 s - - - - IYL = (mn); IYH = (mn+1)
LD dd,(mn) 13 r s - - - - ddl = (mn); ddh = (mn+1)18.3 8-bit Indexed Load and Store
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
LD A,(BC) 6 r s - - - - A = (BC)
LD A,(DE) 6 r s - - - - A = (DE)
LD (BC),A 7 d - - - - (BC) = A
LD (DE),A 7 d - - - - (DE) = A
LD (HL),n 7 d - - - - (HL) = n
LD (HL),r 6 d - - - - (HL) = r = B, C, D, E, H, L, A
LD r,(HL) 5 r s - - - - r = (HL)
LD (IX+d),n 11 d - - - - (IX+d) = n
LD (IX+d),r 10 d - - - - (IX+d) = r
LD r,(IX+d) 9 r s - - - - r = (IX+d)
LD (IY+d),n 11 d - - - - (IY+d) = n
LD (IY+d),r 10 d - - - - (Iy+d) = r
LD r,(IY+d) 9 r s - - - - r = (IY+d)18.4 16-bit Indexed Loads and Stores
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
LD (HL+d),HL 13 d - - - - (HL+d) = L; (HL+d+1) = H
LD HL,(HL+d) 11 r s - - - - L = (HL+d); H = (HL+d+1)
LD (SP+n),HL 11 - - - - (SP+n) = L; (SP+n+1) = H
LD (SP+n),IX 13 - - - - (SP+n) = IXL; (SP+n+1) = IXH
LD (SP+n),IY 13 - - - - (SP+n) = IYL; (SP+n+1) = IYH
LD HL,(SP+n) 9 r - - - - L = (SP+n); H = (SP+n+1)
LD IX,(SP+n) 11 - - - - IXL = (SP+n); IXH = (SP+n+1)
LD IY,(SP+n) 11 - - - - IYL = (SP+n); IYH = (SP+n+1)
LD (IX+d),HL 11 d - - - - (IX+d) = L; (IX+d+1) = H
LD HL,(IX+d) 9 r s - - - - L = (IX+d); H = (IX+d+1)
LD (IY+d),HL 13 d - - - - (IY+d) = L; (IY+d+1) = H
LD HL,(IY+d) 11 r s - - - - L = (IY+d); H = (IY+d+1)18.5 16-bit Load and Store 20-bit Address
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
LDP (HL),HL 12 - - - - (HL) = L; (HL+1) = H.
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP (IX),HL 12 - - - - (IX) = L; (IX+1) = H.
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP (IY),HL 12 - - - - (IY) = L; (IY+1) = H.
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP HL,(HL) 10 - - - - L = (HL); H = (HL+1).
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP HL,(IX) 10 - - - - L = (IX); H = (IX+1).
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP HL,(IY) 10 - - - - L = (IY); H = (IY+1).
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP (mn),HL 15 - - - - (mn) = L; (mn+1) = H.
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP (mn),IX 15 - - - - (mn) = IXL; (mn+1) = IXH.
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP (mn),IY 15 - - - - (mn) = IYL; (mn+1) = IYH.
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP HL,(mn) 13 - - - - L = (mn); H = (mn+1).
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP IX,(mn) 13 - - - - IXL = (mn); IXH = (mn+1).
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])
LDP IY,(mn) 13 - - - - IYL = (mn); IYH = (mn+1).
(Adr[19:16] = A[3:0])Note that the LDP instructions wrap around on a 64K page boundary. Since the LDP instruction operates on two-byte values, the second byte will wrap around and be written at the start of the page if you try to read or write across a page boundary. Thus, if you fetch or store at address 0xn,0xFFFF, you will get the bytes located at 0xn,0xFFFF and 0xn,0x0000 instead of 0xn,0xFFFFand 0x(n+1),0x0000 as you might expect. Therefore, do not use LDP at any physical address ending in 0xFFFF.
18.6 Register to Register Moves
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
LD r,g 2 r - - - - r = g; r,g any of B,
C, D, E, H, L, A
LD A,EIR 4 fr * * - - A = EIR
LD A,IIR 4 fr * * - - A = IIR
LD A,XPC 4 r - - - - A = MMU
LD EIR,A 4 - - - - EIR = A
LD IIR,A 4 - - - - IIR = A
LD XPC,A 4 - - - - XPC = A
LD HL,IX 4 r - - - - HL = IX
LD HL,IY 4 r - - - - HL = IY
LD IX,HL 4 - - - - IX = HL
LD IY,HL 4 - - - - IY = HL
LD SP,HL 2 - - - - SP = HL
LD SP,IX 4 - - - - SP = IX
LD SP,IY 4 - - - - SP = IY
LD dd',BC 4 - - - - dd' = BC (dd': 00-BC',
01-DE', 10-HL')
LD dd',DE 4 - - - - dd' = DE (dd': 00-BC',
01-DE', 10-HL')18.7 Exchange Instructions
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
EX (SP),HL 15 r - - - - H <-> (SP+1); L <-> (SP)
EX (SP),IX 15 - - - - IXH <-> (SP+1); IXL <-> (SP)
EX (SP),IY 15 - - - - IYH <-> (SP+1); IYL <-> (SP)
EX AF,AF' 2 - - - - AF <-> AF'
EX DE',HL 2 s - - - - if (!ALTD) then DE' <-> HL
else DE' <-> HL'
EX DE',HL' 4 s - - - - DE' <-> HL'
EX DE,HL 2 s - - - - if (!ALTD) then DE <-> HL
else DE <-> HL'
EX DE,HL' 4 s - - - - DE <-> HL'
EXX 2 - - - - BC <-> BC'; DE <-> DE';
HL <-> HL'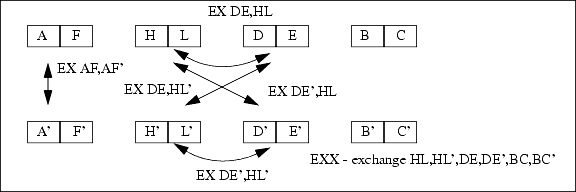
18.8 Stack Manipulation Instructions
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
ADD SP,d 4 f - - - * SP = SP + d -- d=0 to 255
POP IP 7 - - - - IP = (SP); SP = SP+1
POP IX 9 - - - - IXL = (SP); IXH = (SP+1);
SP = SP+2
POP IY 9 - - - - IYL = (SP); IYH = (SP+1);
SP = SP+2
POP zz 7 r - - - - zzl = (SP); zzh = (SP+1);
SP=SP+2 -- zz= BC,DE,HL,AF
PUSH IP 9 - - - - (SP-1) = IP; SP = SP-1
PUSH IX 12 - - - - (SP-1) = IXH; (SP-2) = IXL;
SP = SP-2
PUSH IY 12 - - - - (SP-1) = IYH; (SP-2) = IYL;
SP = SP-2
PUSH zz 10 - - - - (SP-1) = zzh; (SP-2) = zzl;
SP=SP-2 --zz= BC,DE,HL,AF18.9 16-bit Arithmetic and Logical Ops
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
ADC HL,ss 4 fr * * V * HL = HL + ss + CF -- ss=BC,
DE, HL, SP
ADD HL,ss 2 fr - - - * HL = HL + ss
ADD IX,xx 4 f - - - * IX = IX + xx -- xx=BC,
DE, IX, SP
ADD IY,yy 4 f - - - * IY = IY + yy -- yy=BC,
DE, IY, SP
ADD SP,d 4 f - - - * SP = SP + d -- d=0 to 255
AND HL,DE 2 fr * * L 0 HL = HL & DE
AND IX,DE 4 f * * L 0 IX = IX & DE
AND IY,DE 4 f * * L 0 IY = IY & DE
BOOL HL 2 fr * * 0 0 if (HL != 0) HL = 1,
set flags to match HL
BOOL IX 4 f * * 0 0 if (IX != 0) IX = 1
BOOL IY 4 f * * 0 0 if (IY != 0) IY = 1
DEC IX 4 - - - - IX = IX - 1
DEC IY 4 - - - - IY = IY - 1
DEC ss 2 r - - - - ss = ss - 1 -- ss= BC,
DE, HL, SP
INC IX 4 - - - - IX = IX + 1
INC IY 4 - - - - IY = IY + 1
INC ss 2 r - - - - ss = ss + 1 -- ss= BC,
DE, HL, SP
MUL 12 - - - - HL:BC = BC * DE, signed
32 bit result. DE unchanged
OR HL,DE 2 fr * * L 0 HL = HL | DE -- bitwise or
OR IX,DE 4 f * * L 0 IX = IX | DE
OR IY,DE 4 f * * L 0 IY = IY | DE
RL DE 2 fr * * L * {CY,DE} = {DE,CY} --
left shift with CF
RR DE 2 fr * * L * {DE,CY} = {CY,DE}
RR HL 2 fr * * L * {HL,CY} = {CY,HL}
RR IX 4 f * * L * {IX,CY} = {CY,IX}
RR IY 4 f * * L * {IY,CY} = {CY,IY}
SBC HL,ss 4 fr * * V * HL=HL-ss-CY
(cout if (ss-CY)>hl)18.10 8-bit Arithmetic and Logical Ops
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
ADC A,(HL) 5 fr s * * V * A = A + (HL) + CF
ADC A,(IX+d) 9 fr s * * V * A = A + (IX+d) + CF
ADC A,(IY+d) 9 fr s * * V * A = A + (IY+d) + CF
ADC A,n 4 fr * * V * A = A + n + CF
ADC A,r 2 fr * * V * A = A + r + CF
ADD A,(HL) 5 fr s * * V * A = A + (HL)
ADD A,(IX+d) 9 fr s * * V * A = A + (IX+d)
ADD A,(IY+d) 9 fr s * * V * A = A + (IY+d)
ADD A,n 4 fr * * V * A = A + n
ADD A,r 2 fr * * V * A = A + r
AND (HL) 5 fr s * * L 0 A = A & (HL)
AND (IX+d) 9 fr s * * L 0 A = A & (IX+d)
AND (IY+d) 9 fr s * * L 0 A = A & (IY+d)
AND n 4 fr * * L 0 A = A & n
AND r 2 fr * * L 0 A = A & r
CP* (HL) 5 f s * * V * A - (HL)
CP* (IX+d) 9 f s * * V * A - (IX+d)
CP* (IY+d) 9 f s * * V * A - (IY+d)
CP* n 4 f * * V * A - n
CP* r 2 f * * V * A - r
OR (HL) 5 fr s * * L 0 A = A | (HL)
OR (IX+d) 9 fr s * * L 0 A = A | (IX+d)
OR (IY+d) 9 fr s * * L 0 A = A | (IY+d)
OR n 4 fr * * L 0 A = A | n
OR r 2 fr * * L 0 A = A | r
SBC* (IX+d) 9 fr s * * V * A = A - (IX+d) - CY
SBC* (IY+d) 9 fr s * * V * A = A - (IY+d) - CY
SBC* A,(HL) 5 fr s * * V * A = A - (HL) - CY
SBC* A,n 4 fr * * V * A = A-n-CY (cout if (r-CY)>A)
SBC* A,r 2 fr * * V * A = A-r-CY (cout if (r-CY)>A)
SUB (HL) 5 fr s * * V * A = A - (HL)
SUB (IX+d) 9 fr s * * V * A = A - (IX+d)
SUB (IY+d) 9 fr s * * V * A = A - (IY+d)
SUB n 4 fr * * V * A = A - n
SUB r 2 fr * * V * A = A - r
XOR (HL) 5 fr s * * L 0 A = [A & ~(HL)] | [~A & (HL)]
XOR (IX+d) 9 fr s * * L 0 A = [A & ~(IX+d)] | [~A & (IX+d)]
XOR (IY+d) 9 fr s * * L 0 A = [A & ~(IY+d)] | [~A & (IY+d)]
XOR n 4 fr * * L 0 A = [A & ~n] | [~A & n]
XOR r 2 fr * * L 0 A = [A & ~r] | [~A & r]
* SBC and CP instruction output inverted carry. C is set if A<B if the operation or virtual operation is (A-B). Carry is cleared if A>=B. SUB outputs carry in opposite sense from SBC and CP.18.11 8-bit Bit Set, Reset and Test
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
BIT b,(HL) 7 f s - * - - (HL) & bit
BIT b,(IX+d)) 10 f s - * - - (IX+d) & bit
BIT b,(IY+d)) 10 f s - * - - (IY+d) & bit
BIT b,r 4 f - * - - r & bit
RES b,(HL) 10 d - - - - (HL) = (HL) & ~bit
RES b,(IX+d) 13 d - - - - (IX+d) = (IX+d) & ~bit
RES b,(IY+d) 13 d - - - - (IY+d) = (IY+d) & ~bit
RES b,r 4 r - - - - r = r & ~bit
SET b,(HL) 10 b - - - - (HL) = (HL) | bit
SET b,(IX+d) 13 b - - - - (IX+d) = (IX+d) | bit
SET b,(IY+d) 13 b - - - - (IY+d) = (IY+d) | bit
SET b,r 4 r - - - - r = r | bit18.12 8-bit Increment and Decrement
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
DEC (HL) 8 f b * * V - (HL) = (HL) - 1
DEC (IX+d) 12 f b * * V - (IX+d) = (IX+d) -1
DEC (IY+d) 12 f b * * V - (IY+d) = (IY+d) -1
DEC r 2 fr * * V - r = r - 1
INC (HL) 8 f b * * V - (HL) = (HL) + 1
INC (IX+d) 12 f b * * V - (IX+d) = (IX+d) + 1
INC (IY+d) 12 f b * * V - (IY+d) = (IY+d) + 1
INC r 2 fr * * V - r = r + 118.13 8-bit Fast A register Operations
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
CPL 2 r - - - - A = ~A
NEG 4 fr * * V * A = 0 - A
RLA 2 fr - - - * {CY,A} = {A,CY}
RLCA 2 fr - - - * A = {A[6,0],A[7]}; CY = A[7]
RRA 2 fr - - - * {A,CY} = {CY,A}
RRCA 2 fr - - - * A = {A[0],A[7,1]}; CY = A[0]18.14 8-bit Shifts and Rotates
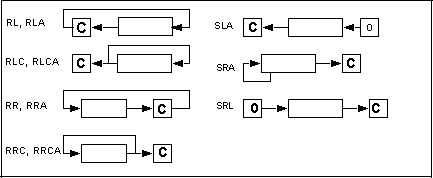
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
RL (HL) 10 f b * * L * {CY,(HL)} = {(HL),CY}
RL (IX+d) 13 f b * * L * {CY,(IX+d)} = {(IX+d),CY}
RL (IY+d) 13 f b * * L * {CY,(IY+d)} = {(IY+d),CY}
RL r 4 fr * * L * {CY,r} = {r,CY}
RLC (HL) 10 f b * * L * (HL) = {(HL)[6,0],(HL)[7]};
CY = (HL)[7]
RLC (IX+d) 13 f b * * L * (IX+d) = {(IX+d)[6,0],
(IX+d)[7]}; CY = (IX+d)[7]
RLC (IY+d) 13 f b * * L * (IY+d) = {(IY+d)[6,0],
(IY+d)[7]}; CY = (IY+d)[7]
RLC r 4 fr * * L * r = {r[6,0],r[7]}; CY = r[7]
RR (HL) 10 f b * * L * {(HL),CY} = {CY,(HL)}
RR (IX+d) 13 f b * * L * {(IX+d),CY} = {CY,(IX+d)}
RR (IY+d) 13 f b * * L * {(IY+d),CY} = {CY,(IY+d)}
RR r 4 fr * * L * {r,CY} = {CY,r}
RRC (HL) 10 f b * * L * (HL) = {(HL)[0],(HL)[7,1]};
CY = (HL)[0]
RRC (IX+d) 13 f b * * L * (IX+d) = {(IX+d)[0],
(IX+d)[7,1]}; CY = (IX+d)[0]
RRC (IY+d) 13 f b * * L * (IY+d) = {(IY+d)[0],(
IY+d)[7,1]}; CY = (IY+d)[0]
RRC r 4 fr * * L * r = {r[0],r[7,1]}; CY = r[0]
SLA (HL) 10 f b * * L * (HL) = {(HL)[6,0],0}; CY =
(HL)[7]
SLA (IX+d) 13 f b * * L * (IX+d) = {(IX+d)[6,0],0};
CY = (IX+d)[7]
SLA (IY+d) 13 f b * * L * (IY+d) = {(IY+d)[6,0],0};
CY = (IY+d)[7]
SLA r 4 fr * * L * r = {r[6,0],0}; CY = r[7]
SRA (HL) 10 f b * * L * (HL) = {(HL)[7],(HL)[7,1]};
CY = (HL)[0]
SRA (IX+d) 13 f b * * L * (IX+d) = {(IX+d)[7],
(IX+d)[7,1]}; CY = (IX+d)[0]
SRA (IY+d) 13 f b * * L * (IY+d) = {(IY+d)[7],
(IY+d)[7,1]}; CY = (IY+d)[0]
SRA r 4 fr * * L * r = {r[7],r[7,1]}; CY = r[0]
SRL (HL) 10 f b * * L * (HL) = {0,(HL)[7,1]};
CY = (HL)[0]
SRL (IX+d) 13 f b * * L * (IX+d) = {0,(IX+d)[7,1]};
CY = (IX+d)[0]
SRL (IY+d) 13 f b * * L * (IY+d) = {0,(IY+d)[7,1]};
CY = (IY+d)[0]
SRL r 4 fr * * L * r = {0,r[7,1]};
CY = r[0]18.15 Instruction Prefixes
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
ALTD 2 - - - - alternate register destinatIn
for next Instruction
IOE 2 - - - - I/O external prefix
IOI 2 - - - - I/O internal prefix18.16 Block Move Instructions
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
LDD 10 d - - * - (DE) = (HL); BC = BC-1;
DE = DE-1; HL = HL-1
LDDR 6+7i d - - * - if {BC != 0} repeat:
LDI 10 d - - * - (DE) = (HL); BC = BC-1;
DE = DE+1; HL = HL+1
LDIR 6+7i d - - * - if {BC != 0} repeat:If any of the block move instructions are prefixed by an I/O prefix, the destination will be in the specified I/O space. Add 1 clock for each iteration for the prefix if the prefix is IOI (internal I/O). If the prefix is IOE, add 2 clocks plus the number of I/O wait states enabled. The V flag is set when BC transitions from 1 to 0. If the V flag is not set another step is performed for the repeating versions of the instructions. Interrupts can occur between different repeats, but not within an iteration equivalent to LDD or LDI. Return from the interrupt is to the first byte of the instruction which is the I/O prefix byte if there is one.
18.17 Control Instructions - Jumps and Calls
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
CALL mn 12 - - - - (SP-1) = PCH; (SP-2) = PCL;
PC = mn; SP = SP-2
DJNZ j 5 r - - - - B = B-1; if {B != 0} PC = PC + j
JP (HL) 4 - - - - PC = HL
JP (IX) 6 - - - - PC = IX
JP (IY) 6 - - - - PC = IY
JP f,mn 7 - - - - if {f} PC = mn
JP mn 7 - - - - PC = mn
JR cc,e 5 - - - - if {cc} PC = PC + e
JR e 5 - - - - PC = PC + e (if e==0 next
seq inst is executed)
LCALL xpc,mn 19 - - - - (SP-1) = XPC; (SP-2) = PCH;
(SP-3) = PCL; XPC=xpc;
PC = mn; SP = (SP-3)
LJP xpc,mn 10 - - - - XPC=xpc; PC = mn
LRET 13 - - - - PCL = (SP); PCH = (SP+1);
XPC = (SP+2); SP = SP+3
RET 8 - - - - PCL = (SP); PCH = (SP+1);
SP = SP+2
RET f 8/2 - - - - if {f} PCL = (SP); PCH =
(SP+1); SP = SP+2
RETI 12 - - - - IP = (SP); PCL = (SP+1);
PCH = (SP+2); SP = SP+3
RST v 10 - - - - (SP-1) = PCH; (SP-2) = PCL;
SP = SP - 2; PC = {R,v)
v=10,18,20,28,38 only18.18 Miscellaneous Instructions
Instruction clk A I S Z V C Operation
CCF 2 f - - - * CF = ~CF
IPSET 0 4 - - - - IP = {IP[5:0], 00}
IPSET 1 4 - - - - IP = {IP[5:0], 01}
IPSET 2 4 - - - - IP = {IP[5:0], 10}
IPSET 3 4 - - - - IP = {IP[5:0], 11}
IPRES 4 - - - - IP = {IP[1:0], IP[7:2]}
LD A,EIR 4 fr * * - - A = EIR
LD A,IIR 4 fr * * - - A = IIR
LD A,XPC 4 r - - - - A = MMU
LD EIR,A 4 - - - - EIR = A
LD IIR,A 4 - - - - IIR = A
LD XPC,A 4 - - - - XPC = A
NOP 2 - - - - No Operation
POP IP 7 - - - - IP = (SP); SP = SP+1
PUSH IP 9 - - - - (SP-1) = IP; SP = SP-1
SCF 2 f - - - 1 CF = 118.19 Privileged Instructions
The privileged instructions are described in this section. Privilege means that an interrupt cannot take place between the privileged instruction and the following instruction.
The three instructions below are privileged.
LD SP,HL ; load the stack pointer
LD SP,IY
LD SP,IXThe instructions to load the stack are privileged so that they can be followed by an instruction to load the stack segment (SSEG) register without the danger of an interrupt taking place with and incorrect association between the stack pointer and the stack segment register. For example,
LD SP,HL
IOI LD (STACKSEG),AThe following instructions are privileged.
IPSET 0 ; shift IP left and set priority 00 in bits 1,0
IPSET 1
IPSET 2
IPSET 3
IPRES ; rotate IP right 2 bits, restoring previous priority
POP IP ; pop IP register from stackThe instructions to modify the IP register are privileged so that they can be followed by a return instructions that is guaranteed to execute before another interrupt takes place. This avoids the possibility of an ever-growing stack.
RETI ; pops IP from stack and then pops return addressThe instruction reti can be used to set both the return address and the IP in a single instruction. If preceded by a LD XPC, a complete jump or call to a computed address can be done with no possible interrupt.
LD A,XPC ; get and set the XPC
LD XPC,AThe instruction LD XPC,A is privileged so that it can be followed by other code setting interrupt priority or program counter without an intervening interrupt.
BIT B,(HL) ; test a bit in memoryThe instruction bit B,(HL) is privileged to make it possible to implement a semaphore without disabling interrupts. The following sequence is used. A bit is a semaphore, and the first task to set the bit owns the semaphore and has a right to manipulate the resources associated with the semaphore.
BIT B,(HL)
SET B,(HL)
JP z,ihaveit
; here I don't have itThe SET instruction has no effect on the flags. Since no interrupt takes place after the BIT instruction, if the flag is zero that means that the semaphore was not set when tested by the bit instruction and that the set instruction has set the semaphore. If an interrupt was allowed between the BIT and set instructions, another routine could set the semaphore and two routines could think that they both owned the semaphore.
| Rabbit Semiconductor www.rabbit.com |